by Jason Tarnow | Jul 2, 2020 | Crime, Criminal Attorney, Legal Rights, Media, Police, Riots, Social Media, Wheels Of Justice
Over the last couple of months, there has been outcry from the public urging the use of BWC’s (Body Worn Cameras) for Canadian law enforcement. Although initially in response to the growing unrest relating to police brutality in the United States, there are echoes of abandoned intentions from Canadian officials dating back at least a few years.
Back in 2015, the Office of the Privacy Commissioner of Canada (“OPCC”) issued a publication regarding the use of BWC by police, in collaboration with privacy agencies in Alberta, New Brunswick and Quebec. The remaining Canadian law enforcement agencies from other provinces and territories acted “in consultation”.
For reference: according to the CBC, there were a total of 2 incidents involving the death of individuals at the hands of law enforcement in New Brunswick between 2012 and 2014, 12 incidents in Quebec, and 14 incidents in Alberta. Interestingly enough, British Columbia (on par with Quebec at 14 deaths) and Ontario (with the highest rate of police violence resulting in death in the country at 25 deaths between 2012 and 2014) were only acting in consultation.
The report hails the effectiveness of BWC to capture high quality images, videos, and audio recordings – so effective, in fact, that the OPCC had grave concerns regarding their ability to capture material that could jeopardize the privacy of innocent and uninvolved bystanders.

The report goes on to tout the value of BWC for evidentiary purposes, including analytics so sophisticated that the material obtained would likely be suitable for biometric comparison – aka, facial recognition.
There is no arguing the fact that the use of BWC by police has implications for the privacy of citizens in their everyday lives – especially since once fitted, citizens would likely expect on-duty officers to have their devices on a continuous basis as opposed to intermittently.
Benefits of BWC include the ability to review interactions between police and the public, recording communications between the police and suspects in the course of an investigation, identifying potential witnesses, and of course recording interactions between police officers. Many criminal cases involve evidence obtained through the use of dash cams, which provide audio from inside a police cruiser and video from the perspective of the driver. The effectiveness of this technology loses value when the investigation takes place outside of a police vehicle, as the audio often fails to capture intelligible communications between police and a suspect, or between officers themselves. Although the dash cam is kept running, the audio portion is often useless when the interactions between police and a suspect take place outside the vehicle, and the windows of the police cruiser are closed, or if the police/suspect leave the immediate area where the audio is successfully captured.
The report indicates that while continuous recording would undoubtedly provide a greater level of accountability for the actions of police, the threat to personal privacy reigns supreme:
“From an accountability perspective, continuous recording may be preferable because it captures an unedited recording of an officer’s actions and the officer cannot be accused of manipulating recordings for his or her own benefit. However, from a privacy perspective, collecting less or no personal information is always the preferred option”
In 2014, the Edmonton Police concluded a pilot project regarding the use of BWC by its officers. The conclusion?:
“The cameras had no effect on police use-of-force incidents and said there was no statistical difference in resolving police complaints”
According to an analysis done by CBC, there were a total of four deaths between 2012 and 2014 relating to officers of the Edmonton Police Service. By comparison, there were 9 deaths in the same period relating to officers of the Toronto Police Service. The results of the Pilot Project may have seen different results in a different jurisdiction.
The Edmonton Police explained that in addition to being ineffective to expose cases of police misconduct, the related expenses were simply unrealistic. Perhaps surprisingly, it’s not the cost of the devices themselves, but the expense to store and manage all of the material collected: somewhere between 6 and 15 million dollars over five years, which also includes hiring personnel qualified for the job.
Finding the balance between accountability, transparency and oversight of police against the protection of privacy for Canadian citizens is a legitimate and profound task – one that cannot be taken lightly. As the calls for BWC in Canadian law enforcement grow louder, and as Canadians revisit the reality of what it is to be privileged in this country, we can only hope that the values of dignity and equality are recognized as being more valuable than the cost of the equipment that very well could save lives.
by Jason Tarnow | Jul 24, 2017 | Crime, Legal Rights, Police, Social Media, Wheels Of Justice

The Vancouver Police Department announced that it will be using a new form of intelligence to stop crime before it happens.
No, it isn’t the formation of the Psychic Task Force. It isn’t any sort of “Big Brother” surveillance method (I think) – rather, the VPD has declared it will be the first law enforcement agency in Canada to utilize a “crime prediction model” that will tip officers off to property-crime offences before they happen.
Unsurprisingly, the public has been given very little information about what this new tool is able to do. So far, all we have been told is that it is a computerized program that was apparently very successful in its 6 month pilot project.
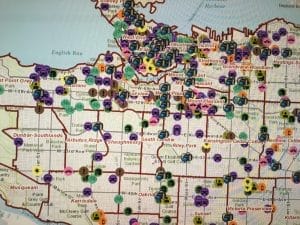
The program identifies both residential and commercial areas that display a high-likelihood for property crime. Surveillance areas are set up within a 100-500 meter perimeter, and officers are then dispatched to those areas for visible public presence.
The presence of police, of course, acts as a deterrent for thieves and vandals.
Interestingly enough, this comes as a further development to the 2015 crime mapping tool developed by the VPD. This interactive map is available to the public, for use by anyone interested in learning more about which areas in Vancouver are deemed higher risk. While many people attribute
While this may seem like a weak method of combatting serious and ongoing theft and vandalism, preventative measures are only deemed necessary once an issue has spiralled out of control.
Charges that police hope to see a reduction in as a result of this new preventative measure:
- Break and Enter
- Break and Enter to commit an Indictable offence
- Theft under $5,000
- Theft over $5,000
- Mischief
- Possession of stolen property
It isn’t unusual to see “petty” crimes, such as minor theft, escalate into more serious situations that can include violent offences as well – for example, a man breaks into a vehicle looking for valuables, but the owner of the vehicle happens to come down to his car as the crime is in progress. An altercation ensues, police attend, and the charges include break & enter, theft, AND assault. By preventing the theft, the entire situation could have been avoided.
Ideally, this tool will aid police in preventing some crimes from happening, but realistically, crimes will still occur in the areas that aren’t padded by police presence.
We are conveniently located in Richmond, B.C. only a few steps away from Brighouse Station on the Canada Line, which brings you from various locations in Metro Vancouver in 20 minutes. We service all areas of the lower mainland (including but not limited to Surrey, New Westminster, Port Coquitlam, North Vancouver, and Abbotsford) the interior of B.C. (including but not limited to Cranbrook, Kelowna, Kamloops, and Salmon Arm), Northern B.C. (including but not limited to Prince George, Prince Rupert, and Quesnel) and in the Yukon Territory where we offer services in Whitehorse, Dawson City, and Old Crow. Contact our office today for your initial consultation.
by Jason Tarnow | Mar 9, 2017 | Crime, Criminal Attorney, Legal Rights, Police, Social Media, Wheels Of Justice
The scales of justice weighed in favour of an Accused woman earlier this week, when the Ontario Superior Court upheld her acquittal of impaired driving related charges in Ontario.
Kimberly McLachlan was acquitted of impaired driving in August 2015 after she succeeded in having evidence inadmissible at Trial – her breathalyzer readings, to be specific. This is known as a Charter application, as it seeks to have evidence excluded based on a breach of a Charter protected right.
Her application was based on the fact that when she taken to the police detachment, where she was required to provide a breathalyzer sample, the arresting officers’ had her stand on a scale so that they could have an accurate record of her weight.
Unfortunately, their attempt to be thorough actually triggered a breach of Ms. McLachlan’s section 8 under the Charter – providing protection against unreasonable search and seizure.
It is not part of standard procedure that the police would weigh a person who has been arrested on suspicion of impaired driving. The Judge confirmed that weighing a person is a violation similar in nature to taking bodily fluids (such as a urine or blood) without a warrant.
It is nuances like this – something seemingly harmless – that will catch the attention of a skilled criminal lawyer. Circumstances like these demonstrate the necessity of hiring a criminal lawyer who is familiar with Charter protected rights.
Impaired driving is a particularly complex offence, with a variety of available defences that must be reviewed in tandem with your unique circumstances. Contact our office today for a consultation that will allow us to come familiar with your situation.



